What is Bitcoin halving ?
Bitcoin halving is an event that occurs approximately every four years, reducing the reward miners receive for adding new blocks to the blockchain by 50%. This event is programmed into Bitcoin’s code to control its supply and mimic the scarcity of precious metals like gold.
How Bitcoin Halving Works
- Block Creation: Bitcoin miners solve complex mathematical problems to create new blocks on the blockchain. For their efforts, they receive a reward in the form of newly minted bitcoins.
- Halving Event: Every 210,000 blocks, the reward for mining a new block is halved. This process continues until all 21 million bitcoins are mined, which is expected to happen around the year 2140.
Historical context of Bitcoin Halving
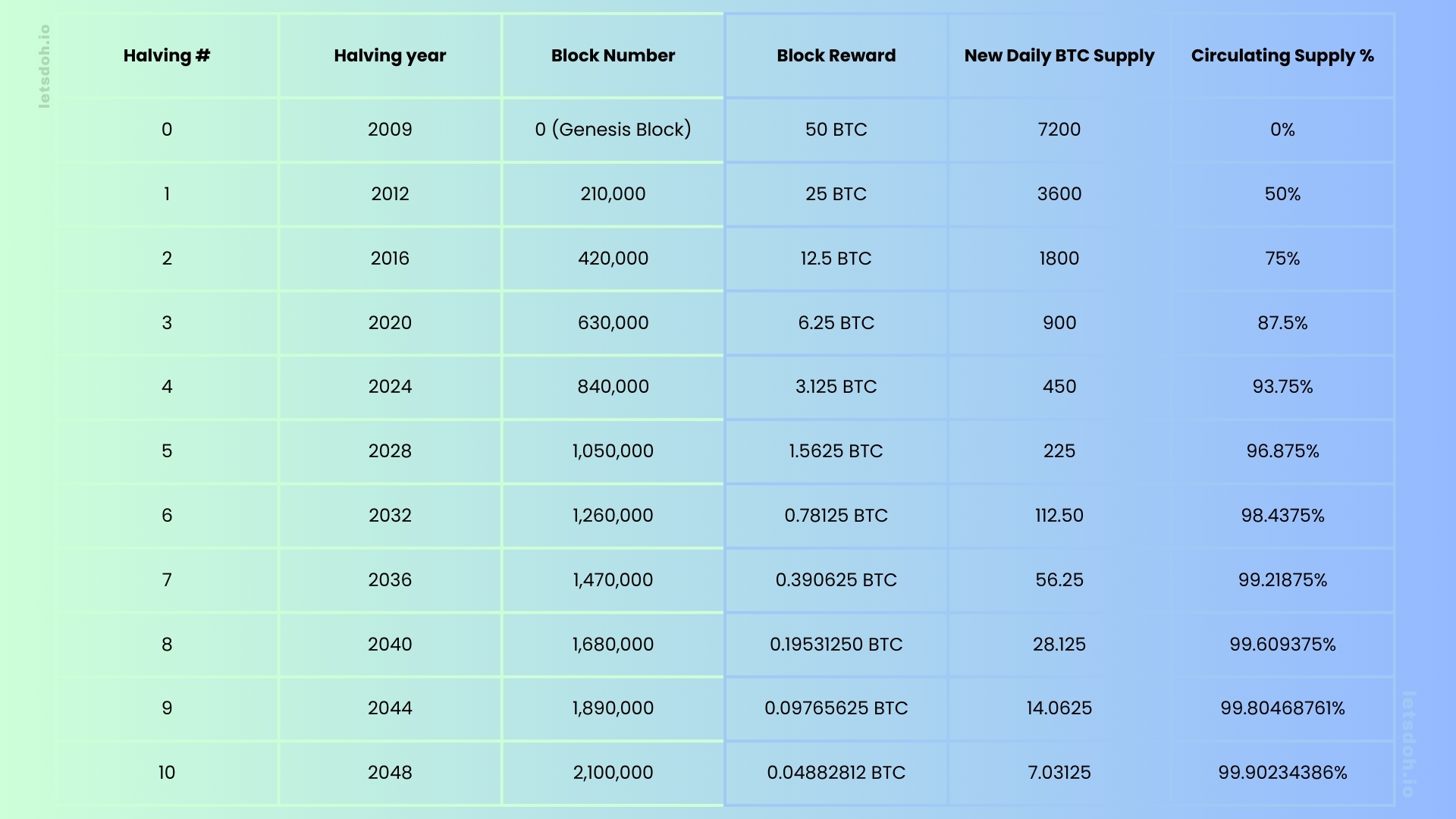
Bitcoin was created by an anonymous person or group of people known as Satoshi Nakamoto. When Bitcoin was launched in 2009, the initial block reward was 50 bitcoins. Since then, there have been three halving events:
- First Halving (2012): Block reward reduced from 50 to 25 bitcoins.
- Second Halving (2016): Block reward reduced from 25 to 12.5 bitcoins.
- Third Halving (2020): Block reward reduced from 12.5 to 6.25 bitcoins.
- Fourth Halving (2024): Block reward reduced from 6.25 to 3.125
Why is Bitcoin halving important?
Scarcity and Value
Bitcoin halving creates artificial scarcity, similar to how precious metals are scarce. By reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are created, halving ensures that the total supply remains limited. This scarcity can drive up the value of Bitcoin over time, as demand for a limited resource increases.
Miner Incentives
Miners play a crucial role in maintaining the Bitcoin network by validating transactions and securing the blockchain. Halving affects their incentives by reducing the rewards they receive. While this can impact miners’ profitability, it also encourages them to become more efficient and use more advanced technology to stay competitive.
Market Impact
Bitcoin halving events have historically led to significant market reactions. Investors and traders often anticipate these events, leading to increased volatility and potential price surges. For instance, after the 2016 halving, Bitcoin’s price surged from around $650 to nearly $20,000 by the end of 2017. Similarly, after the 2020 halving, Bitcoin reached an all-time high of over $60,000 in 2021. It reached a new all-time high of $75,380 in March 2024 a month before the 2024 halving which took place in April.
The challenges and implications of Bitcoin halving events
Price Fluctuations
Bitcoin halving can lead to increased price volatility. As the supply of new bitcoins decreases, the existing demand can drive prices up. However, this is not guaranteed, and other market factors, such as regulatory changes and macroeconomic conditions, also play a role.
Mining Profitability
Reduced block rewards mean miners earn less per block mined. This can affect smaller miners who may struggle with profitability. To stay competitive, miners often need to invest in more efficient hardware and renewable energy sources to reduce operational costs.
Network Security
Miners are essential for maintaining the security of the Bitcoin network. If halving significantly reduces miners’ incentives, some may leave the network, potentially decreasing its security. However, increased Bitcoin prices following halving events can offset this effect by maintaining miner interest and profitability.
Long-Term Investment
For long-term investors, Bitcoin halving can be seen as a positive event that reinforces Bitcoin’s deflationary nature. As the supply of new bitcoins decreases, the limited supply can increase Bitcoin’s appeal as a store of value and hedge against inflation.
Conclusion
Bitcoin halving is a fundamental aspect of Bitcoin’s design, ensuring controlled supply and mimicking the scarcity of precious metals. By reducing block rewards, halving events impact miner incentives, market dynamics, and Bitcoin’s long-term value proposition. Understanding Bitcoin halving is crucial for investors, miners, and anyone interested in the cryptocurrency space.
Enroll on this Free Course


